FCFS scheduling program in C
Here you will learn FCFS scheduling and the example code of FCFS scheduling program in C language.
FCFS Scheduling
FCFS (First Come First Served) is a scheduling algorithm that processes requests in the order in which they are received. This algorithm does not prioritize any requests, but rather processes them in the order in which they arrive. This is the simplest scheduling algorithm and is widely used in operating systems.

FCFS advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ♦ FCFS is simple and easy to implement. ♦ It is also beneficial in a situation where short processes need to be completed quickly since the shorter processes will be completed first. ♦ FCFS does not require any complex data structures or algorithms, making it a good choice for real-time systems. | ♦ FCFS can cause long processes to suffer from starvation, meaning that they may not get enough time to execute. ♦ FCFS does not take into account the priority of processes, so processes with higher priority might not be executed. |
FCFS scheduling example
| Process | Order of arrival | Execution time in msec |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 3 | 15 |
| P2 | 1 | 3 |
| P3 | 2 | 3 |
As shown above,
The waiting time of process P2 is 0
The waiting time of process P3 is 3
The waiting time of process P1 is 6
Average time = (0 + 3 + 6) / 3 = 3 m. sec.
FCFS scheduling program in C
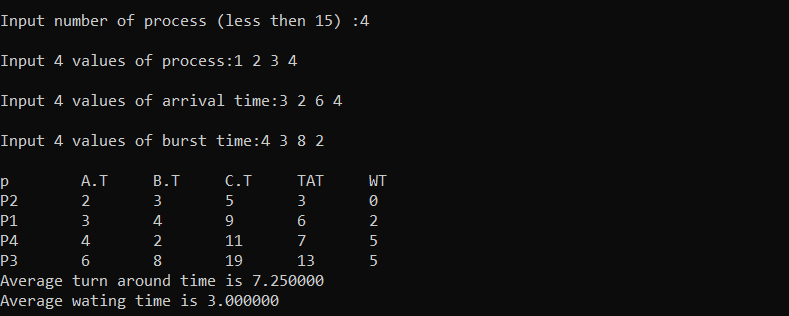
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 | #include<stdio.h> int main() { int num,i,j,process[15],arival_time[15],brust_time[15],c_time[15],turn_around_time[15],waiting_time[15], temp; float awt=0,atat=0; printf("\nInput number of process (less then 15) :"); scanf("%d",&num); printf("\nInput %d values of process:",num); for(i=0;i<num;i++) { scanf("%d",&process[i]); } printf("\nInput %d values of arrival time:",num); for(i=0;i<num;i++) { scanf("%d",&arival_time[i]); } printf("\nInput %d values of burst time:",num); for(i=0;i<num;i++) { scanf("%d",&brust_time[i]); } temp=0; // sorting at,bt, and process according to at for(i=0;i<num;i++) { for(j=0;j<(num-i);j++) { if(arival_time[j]>arival_time[j+1]) { temp=process[j+1]; process[j+1]=process[j]; process[j]=temp; temp=arival_time[j+1]; arival_time[j+1]=arival_time[j]; arival_time[j]=temp; temp=brust_time[j+1]; brust_time[j+1]=brust_time[j]; brust_time[j]=temp; } } } c_time[0]=arival_time[0]+brust_time[0]; for(i=1;i<num;i++) { temp=0; if(c_time[i-1]<arival_time[i]) { temp=arival_time[i]-c_time[i-1]; } c_time[i]=c_time[i-1]+brust_time[i]+temp; } // calculate turn around time and waiting time printf("\np\t A.T\t B.T\t C.T\t TAT\t WT"); for(i=0;i<num;i++) { turn_around_time[i]=c_time[i]-arival_time[i]; waiting_time[i]=turn_around_time[i]-brust_time[i]; atat+=turn_around_time[i]; awt+=waiting_time[i]; } atat=atat/num; awt=awt/num; for(i=0;i<num;i++) { printf("\nP%d\t %d\t %d\t %d \t %d \t %d",process[i],arival_time[i],brust_time[i],c_time[i],turn_around_time[i],waiting_time[i]); } printf("\nAverage turn around time is %f",atat); printf("\nAverage wating time is %f",awt); return 0; } |
Output
Read Also
Priority Scheduling program in C
