Binary Search in C
Here you will learn Binary Search algorithm and the program code of Binary Search in C language by using 4 different ways like with function, with recursion, with arrays and without functions.
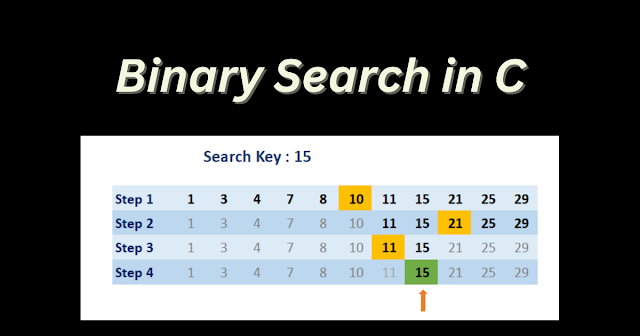
What is Binary Search in C?
Binary search is a search algorithm. It is used for searching an element in a sorted array. It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half until the element is found or the interval is empty.
Scope of Binary Search in C?
Binary search works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half until the desired element is found or the search interval is empty. To perform a binary search in C, the array must be sorted in ascending order.
Algorithm for Binary Search in C
Binary search is a search algorithm that is used to find out the position of a target value within a sorted array. It operates by continually halving the search interval.
The algorithm compares the target value to the value of the array’s middle element. If they are not equal, the half in which the target cannot lie is eliminated and the search continues either in the lower half or in the upper half, until the target value is found.

Binary Search vs Linear Search
| Binary Search | Linear Search |
| (i) Binary search works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half until the element is found. | (i) Linear search is a basic search algorithm that looks through a list of items one by one, in order, until it finds the desired item. |
| (ii) It is complicated and an efficient search algorithm with a time complexity. | (ii) It is simpler and easy to implement than binary search. |
| (iii) It is faster search algorithm than linear search. | (iii) It is slower. |
| (iv) This makes binary search much more efficient (fast) than linear search, which must check each item individually. | (iv) It is the most basic search algorithm and can be used when the data isn’t sorted. |
Different ways to Program Binary Search
Binary Search Program in C using Array
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { int arr[20],n_search,c,num; printf("Enter number of elements (maximum 20) in arrayn"); scanf("%d",&num); printf("Enter %d integer numbern", num); for (c = 0; c < num; c++) scanf("%d",&arr[c]); printf("Enter a number to searchn"); scanf("%d", &n_search); int first, last, mid; first = 0; last = num - 1; mid = (first+last)/2; while (first <= last) { if (arr[mid] < n_search) first = mid + 1; else if (arr[mid] == n_search) { printf("%d is found at %d location.n", n_search, mid+1); break; } else last = mid - 1; mid = (first + last)/2; } if (first > last) printf("%d is not found in the list.n", n_search); return 0; } |
Output

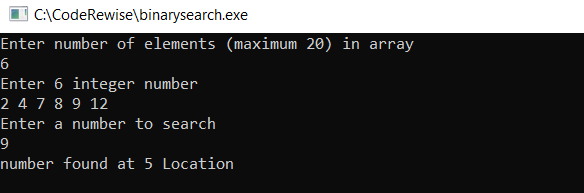
Binary Search Program in C using Function
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | #include <stdio.h> int binary_Search(int array[], int size, int key) { int low = 0; int high = size - 1; while (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; if (array[mid] == key) return mid; else if (array[mid] < key) low = mid + 1; else high = mid - 1; } return -1; } int main() { int array[20],n_search,c,num,key,loc; printf("Enter number of elements (maximum 20) in arrayn"); scanf("%d",&num); printf("Enter %d integer numbern", num); for (c = 0; c < num; c++) scanf("%d",&array[c]); printf("Enter a number to searchn"); scanf("%d", &key); loc=binary_Search(array, num, key); if(loc==-1) printf("number not found in list"); else printf("number found at %d Location n",loc+1); return 0; } |
Output
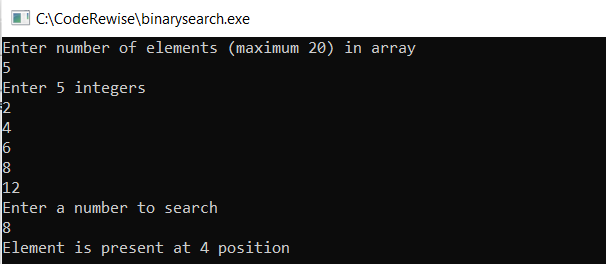
Binary Search Program in C using Recursion
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | //binary search in c recursive #include <stdio.h> int binary_search(int array[], int la, int r, int x) { if (r >= la) { int mid = la + (r - la)/2; if (array[mid] == x) return mid; if (array[mid] > x) return binary_search(array, la, mid-1, x); return binary_search(array, mid+1, r, x); } return -1; } int main(void) { int array[20],x,result,k,num; printf("Enter number of elements (maximum 20) in arrayn"); scanf("%d",&num); printf("Enter %d integersn", num); for (k = 0; k < num; k++) scanf("%d",&array[k]); printf("Enter a number to searchn"); scanf("%d", &x); result = binary_search(array, 0, num-1, x); if(result == -1) printf("Element is not present in array"); else printf("Element is present at %d position", result+1); return 0; } |
Output
Binary Search Program in C without using Function
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { //int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}; int array[20],x,result,k,num; printf("Enter number of elements (maximum 20) in arrayn"); scanf("%d",&num); printf("Enter %d integersn", num); for (k = 0; k < num; k++) scanf("%d",&array[k]); printf("Enter a number to searchn"); scanf("%d", &x); int n, i, beg, last, mid; n = num; beg = 0; last = n-1; while (beg <= last) { mid = (beg + last) / 2; if (array[mid] == x) { printf("%d found at location %d n", x, mid+1); break; } else if (array[mid] < x) beg = mid + 1; else last = mid - 1; } if (beg > last) printf("%d is not present in the array.n", x); return 0; } |
Output

Read Also